
What are zero knowledge proofs and why are they important for blockchain?
When blockchain experienced massive adoption, scalability was one of the pressing challenges that infrastructures built on top of it experienced.
Ethereum’s ability to process just 30 transactions per block obstructed its adoption at enterprise level and that was the point when the need for scaling solutions arose due to delays in rolling out ‘The Merge and Surge” upgrades.
Ever since then, Vitalik Buterin, the founder of Ethereum has considered ZKPs as a feasible solution to scale the Ethereum ecosystem in the longer term. With ETH’s rising market dominance in DeFi and NFTs, sharding must be paired with ZKPs to achieve unprecedented throughput.
At ETH SEOUL event, Vitalik mentioned:
“My opinion is that in the longer term, ZK-Rollups are eventually going to beat Optimistic Roll Ups because they have these fundamental advantages like you don’t need to have a seven-day withdrawal period,”
Buterin said. “In more than 10 years from now or even more, I expect the Rollups to basically be all ZK.”
He emphases that though optimistic rollups are good, ZKP allows faster withdrawals which makes it easier for the users to use dapps built on top of it. Right now, via sharding Ethereum plans to achieve 1500 to 2000 TPS but ZKPs could push that to maybe 50,000 to 100,000 TPS.
Polygon, which is a second layer scaling solution, has been working towards building the next-gen Zk-EVMs which will ensure that developers need not have to develop from scratch when hosting their apps or protocols. For this reason, Polygon has earmarked a $1 billion corpus which will help in the mainstream adoption of ZKP to scale ETH.
Some of its key projects like Miden, Zero, Hermes and Nightfall have already set-up the road ahead to scale the base layer. Through the use of Polygon’s ZKP, developers can right away develop and deploy applications and help Ethereum onboard the next 1 billion users on its ecosystem. Hence saying that ZKPs will be the tech shaping the blockchain space will not be an understatement.
What are Zero Knowledge Proofs?
ZKPs or Zero Knowledge Proof uses cryptography to verify data without actually revealing the data itself. As a result of this trait, ZKPs have revolutionized how data is collected and maintained.
However if you think that ZKPs have been invented post the emergence of blockchain, such is not the case.
In 1985, MIT Researcher Shafi Goldwasser, Silvio Mical and Charles Rackoff conceptualized this and it was widely used in defense back then to verify transactions. Due to this invention, in 1993, they won the Godel Prize for the same.
Through the ZKPs, you can solve any problem without actually revealing the data to the verifier; hence maintaining complete secrecy. The verifier will only know the output thus protecting password and other details and maintaining the integrity of the ecosystem.
In a ZKP set-up, the zero-knowledge proves the completeness, soundness and zero-knowledge or revealing no information to the verifier.
How does ZKP work?
We have an example of a cave to demonstrate how ZKP works.
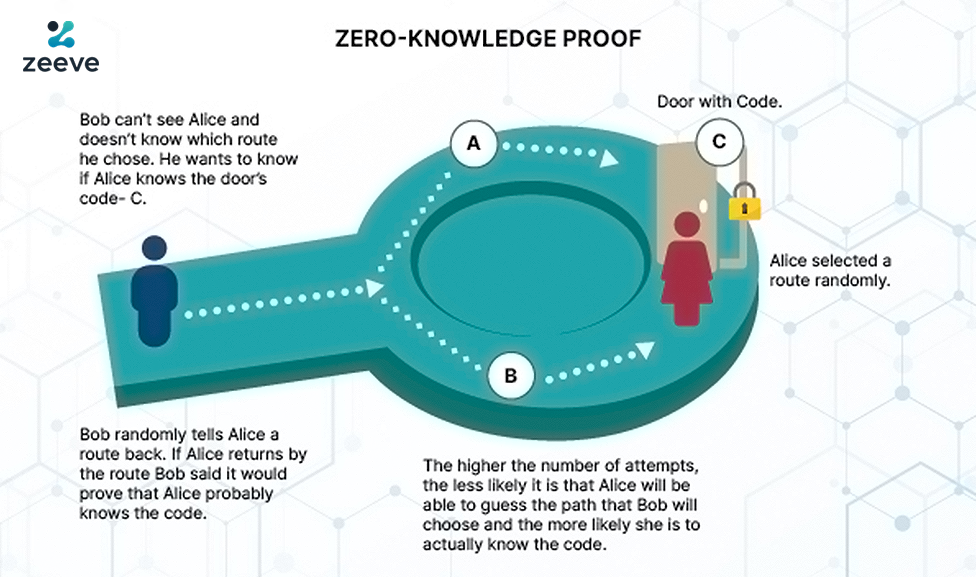
Suppose the cave is circular with two exits A & B and a middle-pass way, C. To cross this door you need to know a Passkey. There are two people: Alice & Bob. Alice wants to prove to Bob that she knows the pass-key without revealing the same.
To prove to the verifier, which is Bob, Alice must enter the cave through Exit A and come out through Exit B.
If she does that, there’s completeness and the passkey used to unlock the inner door, which is C will get the soundness covered.
If Alice comes out of exit door B, it would establish the zero-knowledge at the same time to Bob because Bob don’t know the password and he only tracks if Alice can come out from Exit B or not , and if Alice has made through to the inner door C, it would mean that she may have the pass-key.
The higher the number of attempts, the chances of guess work for Alice will be less, confirming that Alice really knows the pass-key, hence completing the entire process of ZKP to verify a process or a transaction on blockchain.
That’s why zero-knowledge leads to minimal data sharing, thereby, stimulating throughput and scalability of the blockchain.
What ZKP Does For Scaling Blockchain?
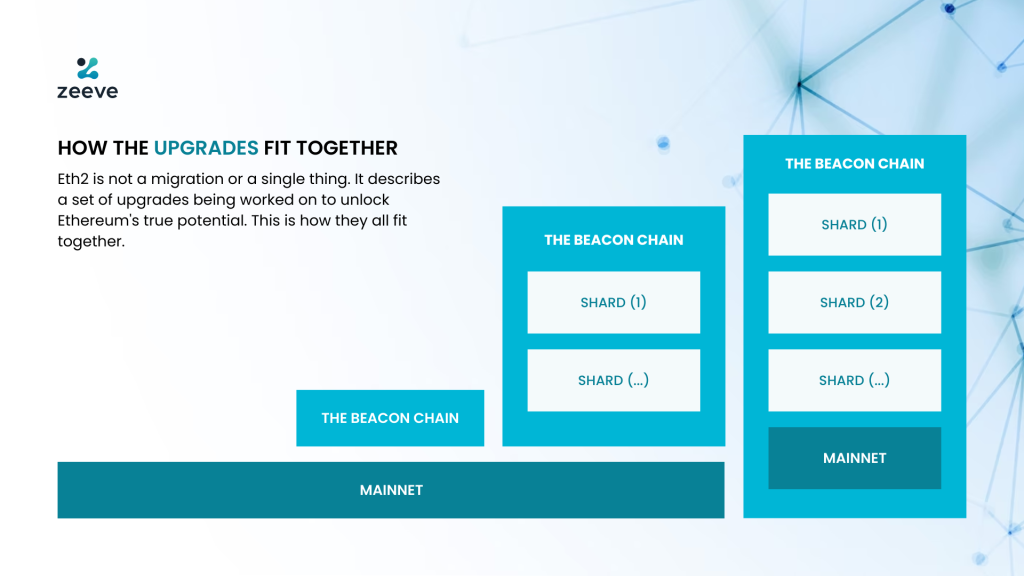
In the above image, you can see that the main-chain is accepting queries from all the shards and propagating the same into blocks on the main-chain, which is Ethereum Layer1 or mainnet.
What if the process continues in the same manner? It is scalable but not super-scalable( That’s the difference between scaling 1500 TPS to 50,000 to 100,000 TPS as per Vitalik Buterin).
What if in one of those shards, there lies transactions which batches another tens and thousands of transactions bundled into 1.
Those data can be verified through a single transaction through root-hashes and Merkle-tree that they are indeed valid. That is something that ZKPs achieve for scaling blockchain.
Here’s how the entire equation changes when ZKPs come into the picture;
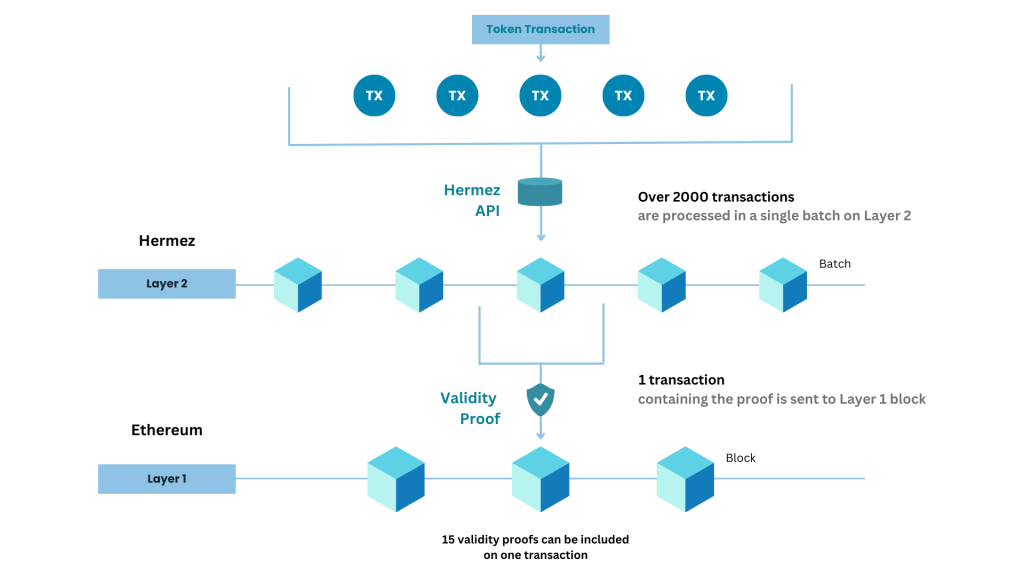
As you can see in the above image, on the Hermez chain, there are 5 shards visible. A typical shard contains 15 TPS; however, what if inside that shard lies a ZKP transaction bundle of over 2000 transactions as shown in the image above.
What if in all the 64 shards of ETH, as many as 10 such transaction batches are pushed. So it makes 2000×10 or 20,000 TPS per second. In this equation, we are speaking of only 10, what if there are 50 or 100. You can expect the scalability it will generate for the main-chain.
But a concern arises that these thousands of transactions awaiting block propagation could be fraudulent. But ZKPs take note of that by posting minimal data to the main-net to query the transaction.
The validators on the main-net can query such transactions through the smart-contract call-data or blobs which doesn’t clog the main chain, which is the Ethereum mainnet.
The state commitment of the ZK-rollups could track any minute changes to the state and report the same to the blobs or call data to verify the transaction.
The validator on the ZKP ecosystem frequently submits information of the change of state to the mainnet through hashed updated account data, rebuilt roll-up Merkle-Tree and a submission of the Merkle-Root to the on-chain contract to eliminate any instance of frauds.
In this way, the transactions are tracked and validated time and again without clogging the mainnet. Thereby achieving the super-scalability for the Ethereum main-net.
How Blockchains Maintain Privacy for Users While Using ZKP?
Public blockchains reveal complete detail of the transaction; for example, the wallet address and the balance transferred or available. But ZKPs completely take unnecessary information not serving the purpose out of the way.
So if you need to know whether an amount was transferred from wallet A to wallet B, ZKPs will only reveal the state of the balance of wallet A or wallet B, without actually exposing the public key of the wallet.
We have already seen in the past that law enforcements have used the flaw of public key cryptography to track essential information to hunt down criminals. It is not bad at all, but this information can be used for deanonymizing some of the prime wallets with very high balance at the same time.
We have seen instances of dusting attacks and other vulnerabilities that public blockchain pose; through the ZKPs, such problems can be mitigated right away for the individuals to enjoy full secrecy of operation on top of the blockchain.
Key developments:
We’re taking a deep dive into Zero Knowledge Proofs to uncover their amazing potential! From ZK snarks and starks, to roll-ups with countless practical uses across industries – these technologies are revolutionizing validation by offering optimal data sharing like never before.
While this technology is incredibly useful, it is difficult to implement as it brings along many complex challenges with applying it safely and ensuring correctness. Vitalik Buterin himself commented on these advancements in Zero knowledge technology saying that
“At the moment, ZK technology is complicated to build. There’s a lot of mental challenge, especially in doing all this safely and ensuring it’s all correct. We have actually started to see ZK-EVM implementations that are almost ready to scale with Ethereum transactions; that is amazing”.
In our upcoming articles we will cover various types of Zero Knowledge Projects, its potential applications, top-tier projects that are presently using Zero Knowledge technology, and many more such things. Let’s take an exciting journey together as we explore the wonders of this tech!







Responses