
Data Availability Layer in Rollups: what is it and why do we need one?
Initially, Layer-2 rollups used to publish their block data on Ethereum, making it accessible for nodes on-chain. This makes Ethreum very congested, which increases transaction cost significantly. As a solution, independent data availability layers have now been introduced, and they are becoming much more popular across L2/L3 rollups and modular blockchains.
For this article, let’s focus on the data availability layer in rollups. We will talk about what the data availability layer exactly means, how it solves the scalability trilemma, and why DA layers are so important.
Let’s first understand data availability.
To better understand the concept of the data availability layer, let’s briefly understand data availability first. DA is the guarantee that all the block producers duly publish their block’s transaction data, allowing all the network participants to download and access these data blocks. These blocks are of the following two main types:
- Block header that contains blockchain’s metadata, such as previous block hash, block number, timestamp, nonce, etc.
- Block body that contains all the list of transactions, containing sender & receiver’s address, amount of tokens being transferred, and digital signatures of involved parties.
Whenever a new block is to be added, the proposer of the block needs to publish both the header and body data, making the information available for the rest of the nodes to verify. This whole process is referred to as data availability.
Now, what is the Data availability layer in rollups?
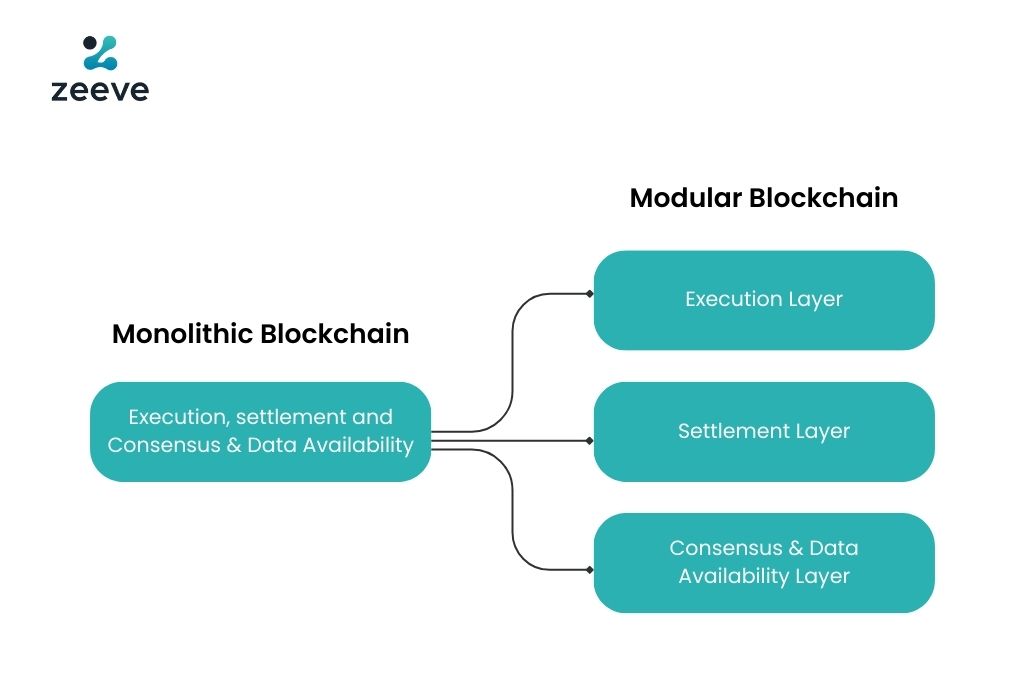
The data availability layer is a vital component of rollups, especially modular ones. DA layer ensures that all kinds of data, such as transaction details, smart contracts data, and other off-chain data, are available to all the nodes on L1, L2, and L3 networks. With a separate DA layer, rollups can have complete control of their mechanism, which allows for better accessibility, transparency, and immutability of data. This DA layer will store all the data and provide consensus for data availability.
Knowing the benefits of moving the DA layer out of the main network (Layer-1) are currently known to all the modular rollup networks, such as Polygon CDK, Arbitrum Orbit, OP Stack, and zkStack, in which every operation such as consensus, settlement, and DA can happen on separate layers. This approach which takes off significant data load from the underlying Layer-1, allowing it to increase throughput capacity, speed, and response time.
We can think of a data availability layer like the recording of a live football game. Imagine a popular football team playing on the field, but not everyone gets the chance to watch it live. Hence, the entire game is recorded and broadcast to people. Here, the data availability layer can be the network that records and broadcasts the football match. This ensures anyone can watch the game and confirm the fair play. Similarly, with the DA layer, any node can replay the blockchain’s history and verify the entire data.
How does the Data Availability Layer work for rollups?
Blockchain rollups; Optimistic and ZK rollups have gained huge traction across web3 projects. However, rollups traditionally store their data in main networks like Ethereum, which increases congestion in their ecosystem. Now, with DA Layer, rollups can maintain a separate blockchain for more streamlined data availability to all the nodes and increased security.
Reliable DA layer providers like Celestia, NEAR, and Avail offer advanced, pluggable data availability layers that developers can use to buid efficient and user-friendly applications. With 100% data availability, the DA layer can support rollups’ integrity and functionality, which ultimately contributes to the goal of improving blockchain scalability.
Hence, we can say that the data availability layer in rollups separates data availability from Layer-1 (for example, Ethereum), which reduces the congestion for enabling higher scalability, better security, and low-cost transactions on the main network. Implementation of the DA layer allows rollups to broadcast transactional data on their own network that would otherwise published on Ethereum. The goal here is to free up significant space from Ethereum and allow it to scale L2s more efficiently.
What makes the Data Availability Layer so important?
Most of the Layer-2 and Layer-3 rollups are built on top of Ethereum and on the equivalent layer-1 ecosystem. The consensus logic of Ethereum dictates that all the transaction data must be available to all the nodes and be independently verifiable. To enable this, rollups earlier were used to publish transaction data as CALLDATA on Ethereum so that nodes can retrieve data easily whenever needed. However, this approach was extremely expensive and resource-intensive. By decoupling the data availability layer from Ethereum, rollups can achieve the following unique benefits:
Enhanced security of blockchain networks:
One of the important advantages of the Data Availability Layer is its potential to ensure the reliable security of rollup networks. By making all the data available and accessible to nodes, the chance of malicious and fraudulent activities becomes almost nil. Further, a DA layer can improve rollup’s performance by allowing faster transaction validation and minimization of network congestion.
Distribured control & scalability:
Having separate DA layers means that a rollup network can experiment with DA and other layers, which makes the ecosystem highly modular & flexible. Also, data availability layers in rollups are optimized to introduce next-gen features; for example, Celestia’s DA supports Data Availability Sampling (DAS) and Namespaced Merkle Trees (NMTs) features that are proven to accelerate a network’s scalability while keeping the battle-tested security intact.
Significant reduction in cost:
As we know, the overgrowing popularity of Ethereum has led to network congestion, which has driven up its transaction fees. Therefore, storing data on a main network like Ethereum is relatively expensive for rollups. Instead, storing calldata on a separate DA layer can reduce the cost significantly. For example, rollups can use NEAR’s DA to store transaction data at approximately 8000x cheaper cost than publishing the same amount of data on Ethereum.
Easy settlement and validation proofs:
The data availability layer ensures that data remains available 24*7 on all the layers of a rollup chain– whether it’s execution, settlement, or consensus layer. This allows for easy resolution of disputes, fraud, and other issues across all the layers. Also, the DA layer can implement an off-chain light client, allowing nodes to confirm data availability without having to download entire blocks.
Simple to interact with:
Although managed parallel to other layers (like the Sequencer and execution layer), data availability layers are simple to interact with. That’s because DA layers are integrated with readily available RPCs that can seamlessly retrieve on-chain data from the whole ecosystem and serve it without any issues.
Exploring different pluggable DA layer solutions
Pluggable DA layer solutions are being increasingly adopted across many blockchains and rollups. Below are some of the leading DA solutions that are pluggable and modular, designed for high-throughout blockchains:
Celestia
Celestia is a modular blockchain network that offers a pluggable, out-of-the-box data availability layer solution that allows web3 developers to plug and play the DA layer into their existing network ecosystem. Data availability sampling (DAS) and Namespaced Merkle trees (NMTs) are the two novel mechanisms that Celestia’s DA layer adopts. DAS enables light nodes for verification of data availability without the need for downloading entire blocks. Whereas NMTs enable settlement and execution layer on Celestia, allwong nodes to download only the transactions which seem relevant to them. With all these unique features, Celestia’s DA layer claims to reduce transaction fees by more than 100x for end users. Prominent rollup ecosystems like Polygon CDK, Arbitrum Orbit, OP Stack, and Starkware are now natively supported in Celestia.
NEAR
NEAR Data availability or NEAR DA layer is another efficient and robust pluggable DA layer solution that simplifies DA layer implementation in your rollup network while lowering the transaction cost considerably. NEAR DA utilizes an off-chain light client that allows nodes to validate that rollup-related data was published on-chain. Further, NEAR uses a Proto-dank sharding approach to increase the throughput capacity of rollups dramatically.
By plugging NEAR DA, rollup networks get cost-effective and reliable data availability. For example, 100kB of calldata on NEAR will cost $0.0033 (As of 2023), and the same calldata will cost $26.22. Ethereum L1 — 8,000 times cheaper!
Avail
Avail is the next big player in the list of pluggable DA layer solutions. Avail’s advanced DA layer is designed to simplify the spinning up of next-generation sovereign rollups. Avail’s DA layer solution can sample from its light client across peer-to-peer networks rather than relying on full nodes. Also, Avail includes innovative mechanisms like data availability sampling (DAS) and next-gen validity proof called KZG commitment. These features ensure DA reduces memory consumption, bandwidth, and storage, thereby making Avail an ideal DA solution for both Optimistic and Zkrollup projects.
How do DA layer solutions work with Zeeve?
Zeeve has included all the leading DA layer solutions– Celestia, NEAR DA, and Avail into its modular rollups-as–a-service (RaaS) stack, enabling web3 projects to easily spin up their modular and high-performance rollup chains in a few clicks with their choice of DA layer. Be it OP Stack, Aritrum Orbit, Polygon CDK, or zkStack; you can add these as your alt DA layer and make your rollups more scalable and cost-efficient.
Zeeve’s RaaS stack is optimized to cut down call data costs to approximately 100 times for all kinds of rollups– Optimistic of Zkrollups. Similar to the DA layer, you can choose Biconomy and Halliday for Account Abstraction (AA), Chainlink for decentralized oracles, Espresso and Radius for Decentralized Sequencer, Subgraph for data indexers, and LayerZero and Router Protocol for interoperability layer. On top of this, Zeeve offers a real-time monitoring dashboard that monitors and manages your rollup networks on cricitial parameters, ensuring its performance and reliable security.
For more information on how Zeeve simplifies the development of modular rollups or to discuss your project-specific requirements, connect with us experts. You can drop your queries via email on this page, or we also have the option to schedule a one-to-one call.







Responses