
Blockchain in Carbon Credit Space: Is Blockchain the savior?
Blockchain in Carbon Credit Space
Can Reduce Global Warming And Save The Planet. Blockchain in the Carbon credit space facilitates an effective way of certifying the carbon credits and beating the challenging issues of climate change.
If you think that blockchain technology is only there to make quick riches and has nothing to do with climate actions, then you may be wrong. You need to relook at the ways in which distributed ledger technology affects the future with its critical role in creating a more sustainable and greener environment. The increased usage of web3 applications over the last few years has moved the blockchain in carbon credit space a few steps closer to achieving one of its objectives of fighting climate change. In fact, the mass adoption of blockchain holds immense scope for turning our world greener and brighter.
Since the beginning of the 21st century, carbon emissions have increased significantly. The Paris Agreement was entered into by all nations with a view to combating climate change and put the best possible efforts. Carbon credit markets were also introduced as an effective method to resolve the greenhouse gas emission reduction problem. In this context, carbon dioxide emission is considered a commodity, thus forming an integral part of the carbon trading system. The United Nations considered carbon offsetting particularly significant for fulfilling the Paris Climate Agreement’s objectives.
The carbon tax or credit were some of the efforts introduced to mitigate this problem. Reports from the New York Times show that greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions trading held enormous scope to turn into the world’s largest commodity market. Furthermore, the World Bank’s report further proves that the carbon emission trading market grew from 10.9 billion USD in 2005 to 143.7 billion USD in 2009, registering an incredible growth of 108% as a result of the Kyoto Protocol taking effect. The recent reports further suggest that the carbon offsets and emissions trading market are growing at 34%, topping at US$215 in 2019. Blockchain in carbon credit space attempts to cut down the role of intermediaries, introduce a transparent process of beating climate change and also resolve other key challenges with the global carbon credits market that failed to make a significant impact in mitigating the greenhouse gas emissions.
Doubts about blockchain having a negative environmental impact
The argument around the most popular cryptocurrency- Bitcoin and its carbon footprint has been raging since its introduction. Many people point out that cryptocurrencies consume a lot of energy and this is why they are not eco-friendly. However, there is another school of thought which shows that blockchain holds immense potential for climate change if the technology is applied in the right way.
A number of experts are of the belief that having the right safeguards can help web3 applications ensure complete environmental integrity. For instance, the proof-of-work consensus driving the Bitcoin network does consume immense amounts of energy but the argument that Bitcoin has a completely negative impact on the environment doesn’t hold much water. The broader ecosystem is gradually shifting towards a cleaner, sustainable and greener future that can yield much lower carbon emissions. Critical environmental solutions can be designed with the help of web3 applications but they need to be designed in the right manner.
The crypto industry and blockchain in carbon credit space is still at their nascent stage and the critics who disgrace these sectors as one causing negative environmental impact are missing the valid point that these industries are still in their early stages. It is also important to recognize the fact that the blockchain has already made its mark despite being in the nascent phase and might soon become a mainstream since most industries are rapidly waking up to the importance it has for progression of the economy and financial ecosystem as a whole. One cannot deny the fact that the industry is witnessing its Eureka moment and the cryptocurrency is no longer a fad but its applications and use cases have gone beyond the conventional streams, rising way above the expectations. Blockchain in carbon credit space facilitates a secure, transparent, trustworthy, efficient and open, and all-feature embracing platform that meets the criteria for deploying the Carbon Credit Markets.
Blockchain in carbon credit space lead to quicker emissions reduction
The blockchain undoubtedly is the disruptor of the modern tech era, expected to push through major changes in the way data is stored and information is distributed. The unique features of the blockchain can bring about major breakthroughs in climate change, also changing the current models of carbon emissions trading and also leading to greater technological advancements and major industrial transformation. Globally, the solutions to the grave problem of climate change have been provided by experts, thereby shifting the focus dramatically from it over the last few years.
The introduction of renewable energy has achieved success in addressing the challenges that climate change brought with it but it scaled up the costs significantly, thereby also leading to slower than expected results. However, a faster reduction of carbon emissions is needed to resolve the distressing climate change at costs much lesser than that of fossil fuels and renewable energy. In such a case, the blockchain in carbon credit space can play a critical role in enhancing the process of carbon trading.
Blockchains in carbon credit space can track and certify carbon credits
The most effective way of certifying the carbon credits is being facilitated by the disruptive technology of blockchains. Businesses are increasingly becoming aware of the environmental impact their processes are having and as such aligning their strategies and processes towards meeting the goal of supporting their country in dealing with climate change and limiting the global warming effects. Currently, Renewable energy certificates (REC) are offered to businesses that represent zero-carbon or fewer carbon emissions.
Enterprises use the RECs to balance their carbon footprints and show compliance with the rules on carbon emissions and environmental standards. In context to the unbundled global trading, in spite of the carbon offset requiring businesses to meet their requirements, RECs fail to ensure that the energy used up has been sourced from the renewable energy sources. Organizations are directing their efforts to utilize this technology to resolve the grave energy challenges.
Firms willing to adopt new solutions for reducing the negative environmental effects can look forward to blockchain adoption. An immutable, tamper-proof, secure, and decentralized blockchain network can use the benefits of the distributed ledger technology and push up the adoption of energy certificates and also facilitate energy usage at par with production. Governments and organizations looking for a greater degree of transparency around carbon credits can experiment with blockchain technology at some point in the near future.
The current landscape of renewable energy credits
Businesses are slowly taking up environmental and sustainability initiatives with different concerns and purposes. Driving towards a more renewable energy business model can save them costs and also help them attract more investors and gain the interest of shareholders. Stakeholders having significant influence in the business funding structure as well as employees are also pushing the enterprises to reduce their carbon footprints and track, report the steps taken to preserve and promote the environment and sustainability. The survey data of global technology buyers conducted by IDC is a testament to the fact that around 69% agree that sustainability efforts are further promoted by their digital infrastructure strategy.
Blockchain in energy credits
With several nations having a deregulated energy market, there is an enhanced demand for decentralized energy providers from the private sector. As avenues open up for the participation of small entities as against the conventional monopolistic or government bodies, unprecedented opportunities have opened up for peer-to-peer (P2P) energy trading firms for the energy exchange and granularity of the energy certificates. For instance, the energy certificates can be exchanged or distributed in smaller program time units (PTUs) or as hourly certificates, being in pace with the clearance and settlement. On the same lines, the introduction of automation and smart meters can save enormous costs and at the same time also simplify the complex carbon accounting process.
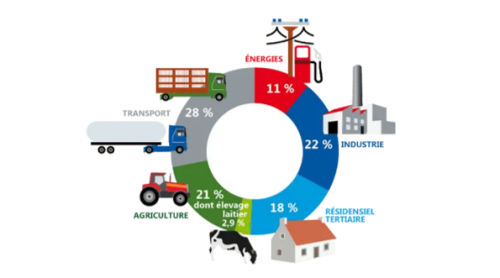
Progressively strict carbon emissions regulations and higher targets for lowering carbon footprints have prompted organizations to redesign and build renewables-based processes. This has further led to an increased surge in the hydrogen project announcements that work in combination with both renewable sectors and the gas. Energy generation using these mixed sources and hydrogen has some carbon emissions that require to be written in the certificates.
There are some set principles and suggestions provided on the standardization of the interoperable protocols from private as well as non-profit organizations seeking primary adapters and contributors to follow as well as contribute to it. There is variance in the deployment for distributing the energy certificates as tokens. Moreover, the implementations for tokenizing certificates are at a nascent stage, thereby leading to differences and disparities in terms of industrial requirements towards interoperability between networks in different countries around the world.
Blockchain in energy credits space
The niche market stakeholders have so far ignored the enormous scope of democratizing the energy procurement process. However, of late, the blockchain adoption in the energy sector and climate change is gaining steam due to its extraordinary features such as transparency, trustworthiness, decentralized, immutable, and verifiable settings that are well recognized by the energy industry communities. The remarkable market trends show that self-sponsored ecosystems are benefiting from the Ethereum-based (ERC-20) solutions and also introducing the dual layer of tokenization in order to facilitate end-users with the access to make the most of their platforms and push up their revenues as well as create exchangeable tokens capturing energy certificates.
Early adopters are assured of incentives as a way to set up a financially stable and also sustainable ecosystem by following the proof-of-stake consensus. A solid example of this is the issuance of green energy certificates to consumers of renewable energy on the decentralized energy supply platform as introduced by the independent EU electricity and gas supply company – Restart Energy Democracy (RED). The consumers and suppliers engaged in peer-to-peer direct trading, while the costs for transactions were also brought down significantly. The most effective strategy on which the RED fell back on was based on the two franchise tiers, the higher of which required the control and ownership of a certain number of tokens.
Power Ledger developed a similar kind of system with its exclusive trade matching algorithms, wherein its consumers are given the free will to transact the available power units fairly without showing bias towards any participant. The native tokens are pinned to a local unit of currency and individual meters are combined in a single transaction. Another trading group that provides an alternative solution on energy certificate exchange via its native tokens is WePower. The group has introduced the financial derivative product with a view to mitigate the risks of corporate power purchasing agreements (PPAs).
Consumer-focused approach towards tokenization of energy credits
With organizations sincerely willing to contribute to the Sustainable Development Goals (SDG), it is important to find alternative and better solutions that can assess the carbon footprints and also support the creation of the ESG reporting. Fractional markets set up by entrepreneurial initiatives for energy credits can complicate the process and lead to slower implementation.
IBM is already working on steps to tokenize the energy certificates using Hyperledger Fabric and Tokens-SDK showcasing the most relevant use case of blockchain in climate change. With the development of this solution, the company aims to bring the current high costs and also simplify the energy trading certificates. With this initiative of energy certificate tokenization of the DLT platform, the group enables the complete disclosure of the amount of energy generated by mixed sources. Additionally, blockchain networks could also store other relevant information such as carbon emissions in the energy supply chain.
The creation of a tokenized energy marketplace will help in facilitating a good variety of trusted certificates in terms of energy types and origin. Suppliers and consumers could also trade their energy certificates with ease and without incurring high costs.
Furthermore, IBM is also developing an energy-friendly solution on private and permissioned-based blockchain technology to get rid of the excess energy consumption by its network operations.
Blockchain promoting environment and sustainability
A few developers have leveraged blockchain in the carbon credit space precisely to back the combined partnership in the sectors of environment and sustainability.
Devvio
This greener cryptocurrency utilizes only a fraction of the energy that is being consumed by Bitcoin. The creation of this greener crypto is done with a view to backing the carbon credit markets and also sustainability efforts. Its performance against ISO standards was monitored by a third party as part of a life cycle assessment (LCA). Reports suggest that the crypto consumes 3.5 billion times far fewer units of energy per transaction than Bitcoin. Avnet and Panduit are partnering with Devvio to help firms connect with the platform attempting the carbon-neutral status. Businesses are seeking to generate carbon credits through a plantation of trees and also undertaking renewable energy infrastructure projects.
Recently, Devvio introduced a unique ESG platform customized to the needs of municipalities. The product suite also lets cities and towns across the globe monitor the carbon emissions generated by their vendor and supplier networks. DevvESG suite has been selected for use by its participating members to pursue sustainability and eco-friendly initiatives in countries such as Canada, the United States, and Mexico.
Algorand
Blockchain-powered platform driven on smart contracts and promoting energy efficiency – Algorand is another positive step towards the direction of sustainability. This blockchain network is unique given the fact that it is carbon negative itself, with the prime aim to counterbalance any carbon emissions. With its tie-up with ClimateTrade, it attained the carbon-neutral status. The collaboration helps firms to track their emissions and offset them.
Furthermore, this blockchain energy-efficient network also developed a unique system that tracks the carbon footprint of a particular number of blocks on the chain, which further helps the platform to assess the equivalent amount of carbon credit, which is also called the Algorand Standard Asset (ASA). The system not only calculates the equivalent amount of carbon credit but also can lock away the ASAs in the green treasury, further allowing Algoraland to stay carbon negative.
Carbon credits as NFTs
Blockchain can be leveraged to mint the carbon credits just as the digital assets or non-fungible tokens called the NFTs. The same blockchain network can be used to trade these tokens and on the basis of the system, the blockchain network can also verify the external carbon credit certificates. A number of new environmental and sustainability initiatives powered by blockchain aim to do just this. Other platforms that are attracting popularity in the blockchain-powered environmental and sustainability projects space are Treedefi and Save Planet Earth (SPE).
Treedefi
Treedefi serves as a token on the Binance exchange rather than acting as the standalone blockchain that intends to set up a development platform. It plants trees with the fees it receives and then sells those as representations just as NFTs. The platform claims to give a third of the transaction fees on the platform towards more plantations of trees.
There is a dashboard on the Treedefi platform enabling viewers to engage in trade and also sell and buy NFT trees while also analyzing the data on each tree’s carbon appropriation. Owning a tree helps the buyer to get CO2 emissions that can help it further counterbalance the carbon emissions. Those tokens can be sold to companies looking to offset their emissions. Users can leverage the safe and secure trading platform and also verify the location of trees, its plantation date and other such relevant information.
Save Planet Earth (SPE / SPEC)
Another ambitious blockchain-powered project that aims at sustainability greater than Treedefi is Save Planet Earth. The project is developed by an expert team possessing a varied range of green technology credentials. The aim of this cryptocurrency project is to plant a billion trees and also develop a wide range of programs such as renewable energy, afforestation, soil regeneration, and recycling to address the issues of global warming and issue of climate change. It also aims to improve marine climate management.
This includes afforestation, reforestation, renewable energy, soil regeneration, recycling, and enhanced marine climate management.
Other uses cases where blockchain in carbon credit space promote sustainability
Greater number of companies are waking up to the numerous benefits that blockchain offers and taking steps towards its faster adoption to make their process more eco-friendly and sustainable. For example: firms are installing software that runs on the blockchain network and provide a quicker, safer, secure, immutable, tamper-proof and effective way to track the supply chains and make them energy-efficient and also more environment-friendly.
Diligent tracing of the raw materials leveraging the blockchain can be useful for the firms to save time and streamline the processes, thus eliminating the complexities and operating at low costs. It is helpful for manufacturing firms to cut down their idle time for the machinery and save significant time for the factories as a whole. In a few cases, blockchain technology adoption can mitigate wasted energy waste and materials.
With blockchain technology offering transparency, security, interoperability, and immutability, companies are implementing the technology to promote zero waste processes and the ecosystem as a whole. Besides monitoring the use of raw materials and making the system energy–efficient, companies can adopt blockchain to recycle materials to reduce the waste and slowly move to the zero-waste system.
Blockchains and energy networks
A great step in the direction of saving the environment is adopting blockchain for energy generation tracking from renewable sources and distribution of the same. Although there are renewable sources of energy such as wind energy, solar energy but there are concerns over the different range of production. There is uncertainty over the energy generation and consumption variability further making it difficult for power grids. Blockchain in carbon credit space offers a transparent and secure way to verify that raw material suppliers are certified and meet the energy requirements on a consistent basis.
The extremely complex energy networks are powered by blockchain technology to smoothly operate and also to help the power production be at par with the energy requirements much easily. It could work well to streamline the renewable energy networks, and also cut down the risk of blackouts while also meeting the need for large contingencies. An energy-efficient system could translate into lower costs for energy, thereby making renewable sources more appealing.
Final thoughts
In today’s world where a lot of focus is being dedicated to environmental impact and sustainability, blockchains play a greater role in such initiatives. Firms genuinely looking to contribute to the greater cause of the environment and produce goods and services to reduce zero-waste can now take recourse to blockchain solutions and make the production process more simple and affordable. Zeeve can help firms incorporate disruptive technology and leverage its benefits for addressing environmental and sustainability concerns.
Blockchain in carbon credit space with its wide range of features such as security, transparency, immutability can provide credible and verifiable eco-friendly solutions. It can offset carbon emissions and also track shipping processes and undertake more complex tasks such as monitoring greenhouse gas emissions as well as the entire supply chain. Firms can leverage the technology to generate transparent energy reports while also maintaining a ledger of carbon credits and carbon emissions. There are a few blockchain networks encouraging sustainability projects to scale up while also staying energy efficient.
Zeeve can help in promoting decentralized financial networks and support sustainability projects. We are here to help companies harness the blockchain technology to improve the existing landscape and bring about more sustainability. With our blockchain node deployment, we also aim to help eco-friendly and sustainable projects draw more investments and manage funding from multiple stakeholders. If you are looking to participate in climate change betterment and carbon credit space then fall back on experts from Zeeve. Give us a call today to support your sustainable blockchain in carbon credit space projects!





This is quite an article; thanks for making it available here.