
The next wave of Polkadot: 06 Major Parachain developments coming in 2024
Parachains are Polkadot’s ground-breaking innovation that has been enabling a wide range of enterprises to develop advanced, future-proof Layer-1 blockchains that are easily customizable for application-specific use cases. Speaking about 2023, it was a cherishing year for Parachain and the monthly active addresses saw notable growth from 104,000 to 2,00,000, and this growth was seen across all the leading Parachains. Plus, a range of interesting upgrades were rolled out for the Parachain ecosystem, such as the introduction of Polkadot-SDK. Now that we are in 2024, let’s talk about the major Polkadot Parachin developments of 2024 and understand how they drive benefits to the entire Parachain ecosystem.
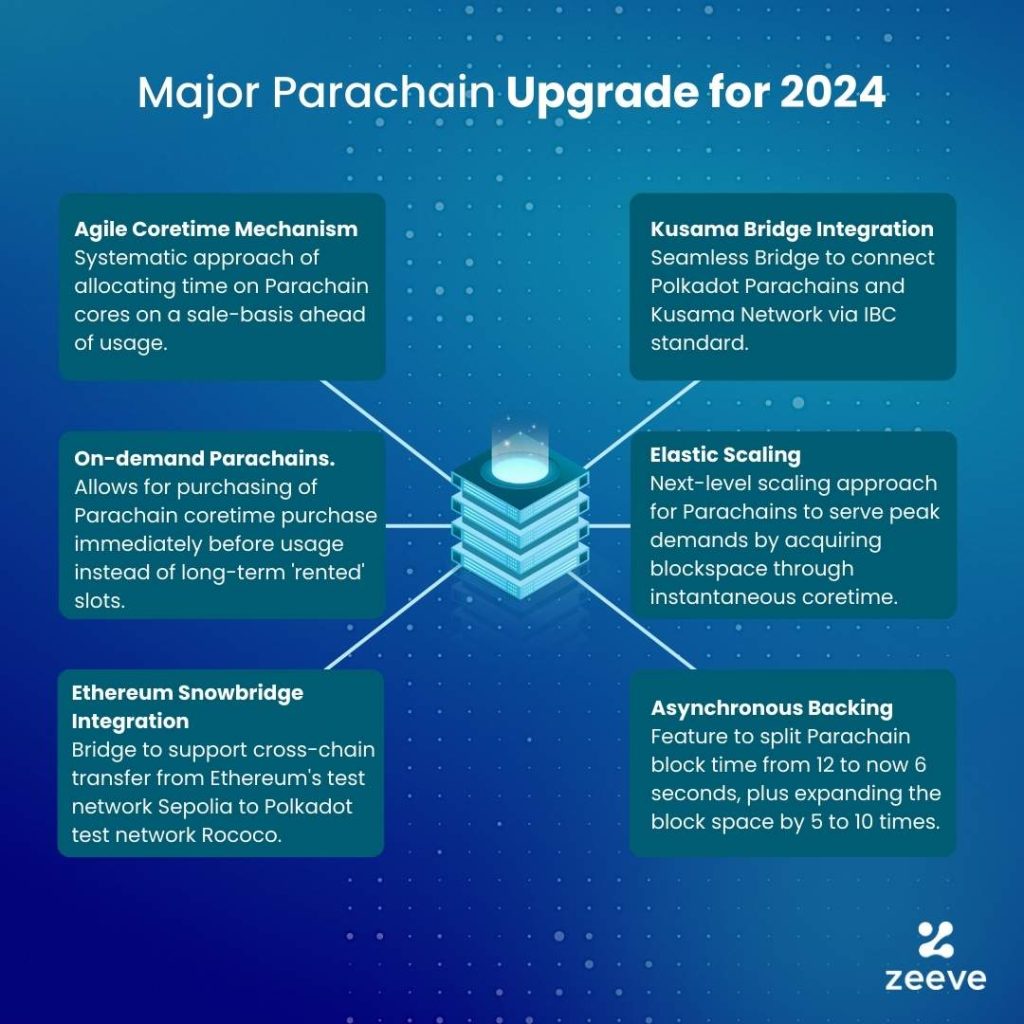
06 Major Polkadot Parachain developments coming in 2024
Based on Polkadot’s official announcements and as described by Gavin Wood in his annual diary that he published in December, 2023, below are the 06 major upgrades coming to Parachains in 2024:
1. Agile Coretime:
Let’s discuss Agile Coretime as the first major Polkadot Parachain developments in 2024. Agile Coretime is a novel idea of Parachain coretime (Duration on Parachain–Polkadot’s key resource) allocation which has been introduced after RFC-1– the first “Request for Comments’ ‘ and an intense development period. Agile Coretime mechanism replaces the traditional auction-based allocation with a unique sale-based approach in which chunks of Coretime are represented as XCM NFTs and are offered to buyers at a more predictable price via monthly sale, ahead of the usage.
Earlier, projects could only lease the Parachain space which included challenges like hard-to-predict deposit, no estimated time of slot allocation. Now, Agile Coretime is eliminating all the previous challenges of auction-based space allocation systems like 2-year contract, high-fluctuation in allocation estimation, and meanwhile making Coretime allocation more predictable, flexible, user-friendly, and economical. For trading of Coretime, marketplaces like Lastic have already been developed, providing ease to the buyers.
What new things Agile Coretime enables?
Coretime-chain:
Coretime-chain is designed to monitor and track record of all the coretime transactions. It’s a sort of specialized ledger which aggregates the activity details for every coretime like who owns how much space, what core has been renowned, which core is sold on bulk, whose ownership is shifting, and many more.
Great Flexibility:
As Agile Coretime replaces the traditional auction-system, users will no longer be forced to lease Parachain blockspace for 6 months to 2 years. Rather, they can instantly specify and get the space they actually need. This situation will save cost, time, and waste of valuable resources.
No need to lock DOT Tokens:
Unlike the old Parachain slot allocation method, Agile Coretime does not require buyers to lock in DOT, which created huge uncertainty and was also discouraging for small projects. Now, they can get the space on-demand with no advance capital investment.
Guarantee of space allocation:
Agile Coretime guarantees space allocation for buyers. Earlier, even when a project successfully gets their desired coretime, the cost of slots after their lease expiry can highly fluctuate due to high demand of Parachains.
Additionally, Agile Coretime offers the following two unique formats for projects through which they can buy Parachain space:
Bulk core time: Exactly what the name suggests, bulk coretime explains the process of buying Coretime in bulk and in advance for future use.
Instantaneous coretime: This format is like SaaS products’ pay-as-you go plan. Projects can buy Coretime and continue paying for its subscription. Plus, this type of Coretime is available for instant needs.
2. On-demand Parachains:
The next big Parachain development in Polkadot’s 2024 bucket is ‘On-Demand Parachains’, which was previously known as Parathread among Polkadot veterans. On-demand Parachains now work with Agile Coretime mechanism and thus represent a highly dynamic acquisition method for Polkadot block space. As we can understand from its name, on-demand Parachains allow projects to buy coretime immediately whenever there’s a requirement for transactions. The need of opting for longtime “rented” blockspace will no longer be relevant. Instead, On-demand Parachain model will be applicable where buyers contribute Coretime into a shared pool and from that pool anyone can buy required Coretime in an instance. Besides Agile Coretime, On-demand Parachains will set a new standard for Polkadot’s space utilization process. As discussed, On-demand Parachains are backed with Agile Coretime mechanism. Therefore, the same two space selling formats– Bulk core time and Instantaneous coretime will work for ODPs as well.
What Problem On-Demand Parachains aim to solve?
Before On-demand Parachains (ODPs), projects had the only option to secure block space for a certain period; e.g one 2 years. Plus, they are required to author a new block every 12 seconds throughout the duration you own the slot. While this guaranteed ability or requirement to author block in 12 seconds is an essential feature for high-traction applications, the same can also result in wastage of computational resources from the perspective of new projects that do not see very high volumes of transactions as they are just starting out. On-demand Parachains puts an end to this 12-seconds block authoring method and instead allows collator-based ordering of Core when there’s a demand.
3. Elastic Scaling:
Elastic scaling, which can also be called on-demand scaling, is a feature that will allow Parachains to occupy multiple cores simultaneously, enabling them to achieve scalability beyond one single core. Simply put, Elastic scaling optimizes Parachain network’s performance by adjusting its resource allocation in line with the scaling demand. As we know, the demand for blockspace in applications will peak and fall. The peak demand here can be catered by acquiring additional coretime with instantaneous coretime of Elastic Scaling. However, for more predictable demand, applications should ideally acquire blockspace in bulk.
How Elastic Scaling works?
The main technology powering Elastic scaling is Agile Coretime that we have discussed already. With Agile Coretime, Parachains get the flexibility to scale dynamically– be it up or down based on needs. For example, if your application needs higher scalability, you can add more cores. Whereas, if the traffic volume goes down, you can exclude core to reduce scalability, thus preventing the situation of ‘Empty Blocks’ which is a major challenge for blockchains nowadays.
4. Asynchronous Backing:
Asynchronous Backing is a very crucial upgrade on Parachain’s consensus protocol, for which the announcement was made by Polkadot developers at the sub0 developer conference held in Lisbon. Async backing is essentially designed to split the existing Parachain block time from 12 to now 6 seconds and meanwhile expand the block space on each block by at least 5 to 10 times. As of now, asynchronous Backing is live on Kusama, plus it’s supported on Rococo testnet and will soon be pushed on to production.
Elastic scaling and instantaneous coretime are the two main technologies that powers asynchronous backing, enabling greater flexibility into Parachains for future scaling. Parity’s lead engineer, Sophia Gold earlier made a statement saying that the Polkadot team has created a credible roadmap to scale Parachains for massive scalability. Launching the asynchronous Backing feature is one such effort that we have made to enable endless scalability in Parachains and expand our ecosystem to 1,000 Parachains by the end of 2024.
Key advantages of Asynchronous Backing:
- 2x higher throughput or 2x lower latency for all the Parachains.
- Allows 4x more data for a parablock
- Enable all the Collators to submit parablocks in advance for backing desired groups.
- Ease for Collators as they have the flexibility to build parablocks in advance.
- Greater efficiency and notable boost in scalability.
- Less or almost zero wastage of empty (unused) blockspace.
5. Ethereum Snowbridge:
Addition of Snowbride into Polkadot is making waves across the Parachain community. On 16th of January, Snowbridge developer– Clara announced on X Platform that their team has deployed Snowbridge successfully on Rococo public testnet. Hence, users can test the usability of the bridge by performing cross-chain transfer of tokens back and forth from Ethereum Sepolia to AssetHub Rococo.
Snowbridge is a general-purpose, fully decentralized, and trustless bridge between Polkadot and Ethereum designed for enabling cross-chain asset transfer and compatibility. Further, Snowbridge eventually aims to be a common-good bridge launched on BridgeHub Parachain.
Components upholding Snowbridge:
BridgeHub
The Parity team, in alliance with Web3 Foundation and Snowfork has launched their common-good BridgeHub on Kusama. This bridge hub hosts several bridges between other chains, including Ethereum & Kusama. Bridge hub implements multiple unique pallets to be able to work and allow cross-chain asset transfer, which are:
- InboundQueue- Pallet designed for accepting all the inbound messages from the Ethereum blockchain.
- OutboundQueue– Pallet designed for accepting all the outbound messages to the Ethereum blockchain.
- EthereumBeaconClient- This pallet works with a Light Client that is responsible for tracking Ethereum’s Beacon chain and verifying all the inbound messages submitted on InboundQueue pallet.
- System– Pallet that takes overall responsibility of the bridge, plus it provides basic system functionality to ensure its seamless operation.
Ethereum-side components
Gateway- The Ethereum-side of the bridge hub is organized with a central gateway which is responsible for receiving, verification, and dispatch of inbound Polkadot’s messages. Plus, it accepts outbound messages to deliver to Polkadot as well as implement high–level features; e.g. token transfer.
Agent- Agent contract’s instances work as proxies for the consensus systems of Polkadot. Developers can initiate creation of agents in a permissionless way by calling the extrinsic: EthereumSystem::create_agent on the Parachain’s BridgeHub.
BeefyClient- Verifies Polkadot Consensus by implementing a light client.
6. Kusama Bridge:
Last but very important Polkaot Parachain development in 2024 is the upcoming Kusama→Polkadot bridge. Since the start, Kusama has been optimized to receive messages from non-Parachain or external chains using Substrate pallets. This same Substrate instance will be utilized in the Kusama to Polkadot bridge, which will be implemented either as a system-level Pararchain or as the community-operated Parachains.
Based on the most recent update, the Kusama bridge is live and is bridging Rococo <> Westend testnets. The bridge is deployed on the Rococo Bridge Hub and Westend Bridge Hub chains, and is configured to bridge XCM messages between Rococo Asset Hub and Westend Asset Hub. This means you can use XCM to transfer ROC and WND tokens across both chains seamlessly.
With these same capabilities, the bridge will be deployed on Polkadot and Kusama as soon as the on-chain runtimes get upgraded to release Runtimes 1.1.2. The estimate for the bridge being live is within the first half of March, 2024 (as confirmed by Polkadot’s officials).
Apart from these six major developments, Polkadot is expecting a few more upgrades in 2024 and beyond. This may include expansion of XCM and DAO primitives, multi-asset sub-treasuries, an innovative consensus for block production– Sassafras, and a different recent RFC, known as CoreJam.
Launch your own Parachains with Zeeve’s Open-source tools, Low-code tools in minutes
Zeeve is committed to simplifying blockchain deployment for everyone. For Parachains, Zeeve Rollups-as-a-service (RaaS) stack mainly offers two open-source tools— Wrench and Larch, complete with an abstraction layer over the complex method of testing and deploying custom Parachains.
Wrench is an intuitive and easy-to-use tool designed to launch a production-grade Parachain on the rococo-local. Wrench offers a comprehensive toolkit for setting up all kinds of Parachains– be it a multi-node, managed, or distributed Parachain Testnet, integrated with analytics, monitoring capabilities, and real-time alerts.
Larch is focused on Parachain testing. It’s an innovative GUI frontend that automates the creation, management, and testing approach of the Zombienet. Using Larch’s comprehensive dashboard, developers can quickly set up relay chains and parachains just in a few clicks, with no need to manually write command lines or create .toml or .yaml files.
For more information about Zeeve’s Parachain-related services or Zeeve RaaS, connect with our experts. You can simply drop your queries via mail on this page or for a detailed discussion, there’s an option for scheduling one-to-one calls.







Responses